
Contents
- 1 Understanding Schizophrenia Symptoms Causes and Support Guide
- 2 What Is Schizophrenia
- 3 Major Symptom Categories of Schizophrenia
- 4 Positive Symptoms
- 5 Negative Symptoms
- 6 Cognitive Symptoms
- 7 What Causes Schizophrenia
- 8 Genetic Factors
- 9 Brain Chemistry and Structure
- 10 Environmental Influences
- 11 Early Warning Signs of Schizophrenia
- 12 Treatment Options for Schizophrenia
- 13 Medication Treatment
- 14 Therapy and Counseling
- 15 Lifestyle Support and Healthy Habits
- 16 How to Support Someone with Schizophrenia
- 17 Conclusion
- 18 Final Thoughts
- 19 FAQ Section for Understanding Schizophrenia Symptoms Causes and Support
- 20 Related Mental Health References and Trusted Resources
- 21 More Articles From The Mental Health Blogger
Understanding Schizophrenia Symptoms Causes and Support Guide
Learn the key symptoms of schizophrenia, what causes it, and how to find the right support. This clear guide helps readers understand early signs, risk factors, treatment options, and supportive resources for managing schizophrenia.
Schizophrenia is one of the most misunderstood mental health conditions in the world. Many people grow up hearing myths that paint a frightening picture. The truth is very different. Schizophrenia is a real medical condition that affects how a person thinks, feels, and interprets reality.
When you approach it with compassion, you begin to understand the human experience behind the symptoms.
This guide gives you a clear explanation of schizophrenia in simple language so you can recognize the symptoms, understand the causes, and know the best ways to support someone who lives with this condition.
The disorder can disrupt daily life in powerful ways. A person may hear voices, feel confused about what is real, or withdraw from the people they love. These changes can feel overwhelming.
With the right treatment and support, many people reach stability and live meaningful lives. The key is understanding what schizophrenia looks like, what triggers symptoms, and what treatments help.
This article goes step by step through each part of the disorder. You will learn about symptom categories, genetic factors, brain chemistry, early warning signs, support techniques, and long term recovery strategies.
Keep reading below to learn more about the process of “Understanding Schizophrenia: Symptoms, Causes, and Support.”
What Is Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a chronic mental health condition that affects how a person processes information. The condition changes how someone interprets reality.
It can influence thoughts, emotions, communication, and behavior. The disorder does not appear in the same way for every person. Some experience mild symptoms. Others experience intense episodes that require medical care.
How Schizophrenia Develops Over Time
Schizophrenia usually develops slowly. Many people start to show early signs in their late teens or early twenties. It rarely appears suddenly.
The early signs often look like withdrawal or emotional changes. Over time, the symptoms may become clearer. This gradual development explains why early detection is so important.
How Schizophrenia Impacts Daily Life
Daily life becomes more complicated when symptoms appear. Relationships may feel harder to maintain. Work responsibilities may feel overwhelming.
School performance may change quickly. People often feel confused by their own thoughts and feelings. These changes can create stress and fear.
A person may also worry about how others see them. Stigma can make symptoms worse because it adds shame and isolation.
With treatment, education, and support, a person can regain confidence and build new routines that support long term wellness.
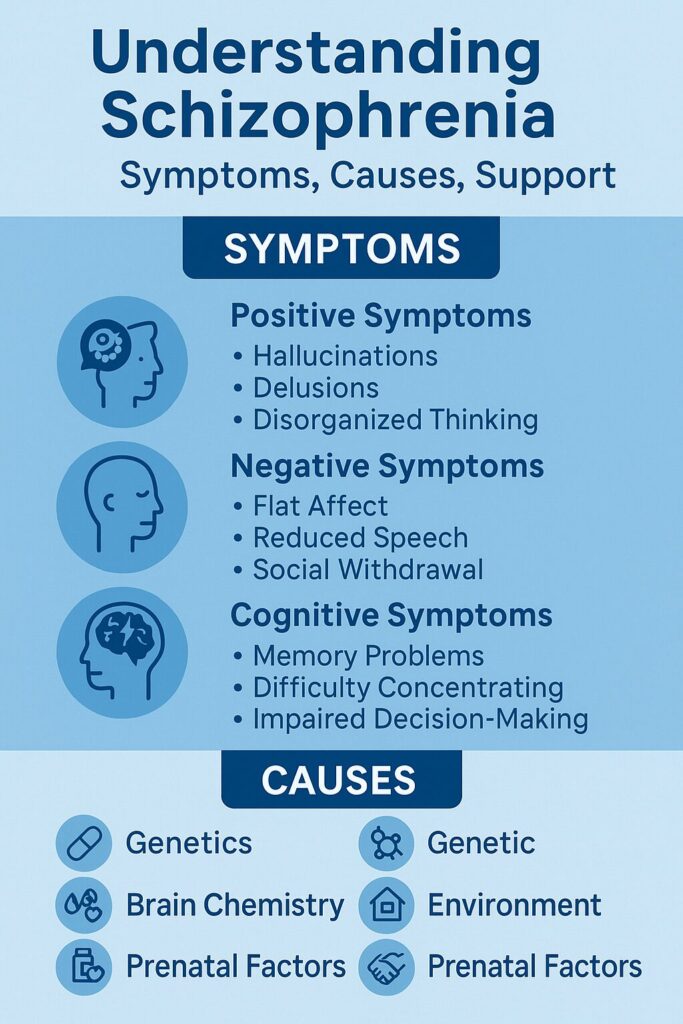
Major Symptom Categories of Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia symptoms fall into three major categories. Each category reveals a different part of the disorder. Understanding these categories helps you see the full picture.
Positive Symptoms
Positive symptoms refer to behaviors or experiences that appear in addition to typical functioning.
Detailed Positive Symptoms
Hallucinations
Hallucinations are experiences that involve sensing things that are not there.
Longer details include:
- Hearing voices that speak clearly and directly
- Seeing shapes or figures that others cannot see
- Feeling sensations on the skin without a physical cause
- Smelling scents or chemicals that are not present
- Experiencing these sensations during stressful moments
These hallucinations often feel completely real. They can cause fear, confusion, or emotional distress.
Delusions
Delusions involve strong beliefs that are not based on reality.
Expanded information:
- A person may believe someone is monitoring them
- They may think strangers can read their mind
- They may believe they have a special mission or gift
- They may develop strong suspicions about family or friends
- These beliefs remain strong even with evidence that proves otherwise
Delusions can create distance between a person and the world around them, which can lead to isolation.
Disorganized Thinking and Speech
Disorganized thinking affects how a person expresses their thoughts.
Detailed signs include:
- Difficulty staying on one topic
- Words that are loosely connected
- Conversations that feel confusing
- Sudden changes in thought direction
- Thoughts that move too quickly to express clearly
This makes communication challenging and sometimes stressful.
Negative Symptoms
Negative symptoms involve the loss of typical behaviors or emotional responses.
Reduced Emotional Expression
A person may appear flat or distant. Their facial expressions may not match their emotions. They may speak in a quiet or monotone voice. This does not mean they lack emotion. They simply struggle to express it.
Lack of Motivation
Daily routines feel draining. Starting simple tasks feels difficult. Activities that once brought joy may feel exhausting. This lack of motivation can affect everything from hygiene to relationships.
Social Withdrawal
A person may pull away from family or friends. Social settings may feel overwhelming. They may worry about being judged or misunderstood. Withdrawal often increases as symptoms intensify.
Cognitive Symptoms
Cognitive symptoms affect memory, concentration, and problem solving.
Detailed Cognitive Symptoms
Difficulty Focusing
A person may struggle to complete tasks or follow conversations. Thoughts may become scattered or interrupted.
Working Memory Challenges
Working memory helps you hold information long enough to use it. When this is affected, simple tasks like following steps or recalling instructions become harder.
Slow Information Processing
Complex information takes longer to understand. This can make learning, decision making, and planning more difficult.
What Causes Schizophrenia
The causes of schizophrenia are complex. Researchers believe that multiple factors work together.
Schizophrenia develops from a combination of genetic factors, brain chemistry changes, and environmental influences that shape how the brain processes thoughts and emotions. Plus other factors.
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a strong role. If a close family member has schizophrenia, the risk increases. This does not mean the disorder is guaranteed. It only means the likelihood is higher. Many people with a family history never develop the condition.
Additional Genetic Insights
- Schizophrenia involves many genes, not just one
- Different genes influence brain development
- Genes may interact with stress or trauma
These genetic patterns help explain why symptoms vary widely.
Brain Chemistry and Structure
Schizophrenia is linked to changes in brain chemicals.
Key Details
- Dopamine imbalance can affect thought patterns
- Glutamate changes may influence memory
- Brain imaging shows structural differences
- Parts of the brain related to emotion and perception may change
- These differences develop slowly over time
These changes explain why symptoms involve both thinking and emotion.
Environmental Influences
Environmental events can also contribute to schizophrenia.
Detailed Environmental Factors
- Exposure to high stress during childhood
- Traumatic experiences that change emotional development
- Prenatal infections
- Poor nutrition during pregnancy
- Complications during birth
- Limited access to mental health resources
- Substance use during adolescence
These factors combine with genetics to increase the risk.
Early Warning Signs of Schizophrenia
Early symptoms often appear before a full episode. This phase is known as the prodromal period.
Detailed Early Warning Signs
Behavioral Changes
- Withdrawal from friends
- Sudden changes in habits
- Loss of interest in activities
- Decreased motivation
Emotional Changes
- Flat mood
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Sudden mood drops
Cognitive Changes
- Trouble focusing
- Confusing thoughts
- Slower thinking
- Trouble understanding information
Social Changes
- Avoiding conversations
- Feeling suspicious of others
- Difficulty understanding social cues
Early intervention can greatly improve long term outcomes.
Treatment Options for Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is treatable. Many people lead meaningful lives with the right support and the right medications.
Medication Treatment
Medication helps manage positive symptoms. The key to success is to find the right medications that work for you.
Detailed Medication Considerations
- Antipsychotic medications reduce hallucinations
- They help limit delusions
- They stabilize thought patterns
- Medication plans are personalized
- Regular checkups are important for safety
- Doctors adjust doses based on progress
Medication works best when combined with therapy and social support.
Therapy and Counseling
Therapy provides emotional guidance and structure.
Common Therapy Types
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- Helps identify thought patterns
- Provides coping strategies
- Improves emotional regulation
- Makes stressful situations easier to manage
Social Skills Therapy
- Helps improve communication
- Supports relationship building
- Encourages confidence in social settings
Family Therapy
- Teaches families how to respond calmly
- Reduces stress at home
- Creates understanding and unity
- Helps families learn healthier communication approaches
Lifestyle Support and Healthy Habits
Healthy routines improve treatment outcomes.
Detailed Lifestyle Strategies
- Regular sleep patterns reduce stress
- Daily structure helps manage symptoms
- Balanced nutrition supports mental clarity
- Exercise encourages emotional regulation
- Mindfulness reduces confusion and worry
- Avoiding substances reduces symptom triggers
- Support groups create connection and belonging
Each habit adds strength to long term recovery.
How to Support Someone with Schizophrenia
Support from others is essential. Having a support system for someone with schizophrenia is a very important aspect in helping the diagnosed person.
Detailed Support Strategies
Listen Without Judgment
People with schizophrenia need a safe space. Listening helps them feel understood. Avoid correcting their experiences. Respect their feelings and fears.
Encourage Treatment Gently
Support appointments. Offer reminders. Celebrate progress. Avoid pressure or criticism.
Create a Calm Home Environment
A peaceful environment reduces stress. Use soft lighting. Maintain predictable routines. Reduce loud noise or conflict.
Provide Emotional Encouragement
- Offer reassurance
- Express understanding
- Praise small wins
- Remind them they are not alone
Learn as Much as Possible
Education is powerful. When you understand schizophrenia, you can support with confidence.
Conclusion
Schizophrenia is a complex but manageable condition. The symptoms affect thoughts, emotions, and perception, yet treatment and support give people the chance to live stable and fulfilling lives.
Understanding the causes and symptoms helps remove fear. It also builds compassion. When you support someone with patience, education, and kindness, you help them take important steps toward healing and stability.
Final Thoughts
Schizophrenia does not define a person. It is only one part of their journey. When you approach this condition with knowledge and compassion, you become a source of strength.
You learn how to recognize early signs, how to support treatment, and how to offer hope.
The more we understand mental health, the more we reduce stigma and build a future where everyone feels seen and supported.
FAQ Section for Understanding Schizophrenia Symptoms Causes and Support
What are the first early signs of schizophrenia that people usually notice
Early signs include social withdrawal, loss of interest in activities, changes in sleep patterns, difficulty concentrating, and unusual thoughts. A person may seem more anxious or confused. These early changes often appear slowly and may look similar to stress or depression. When several early signs appear at the same time, it is helpful to seek a mental health evaluation.
What symptoms help doctors diagnose schizophrenia
Doctors look for symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, confused thinking, disorganized speech, flat emotions, low motivation, and cognitive difficulties. These symptoms must last for a significant period of time. A mental health professional uses a full evaluation to confirm the diagnosis.
What causes schizophrenia in most people
Schizophrenia develops from a combination of genetic factors, brain chemistry, and environmental influences. Family history increases risk. Changes in dopamine and glutamate may play a role. Stress, trauma, complications during pregnancy, and prenatal infections can also contribute. No single cause explains every case.
Can schizophrenia be treated successfully
Yes. Treatment can greatly reduce symptoms. Most treatment plans include antipsychotic medication, therapy, lifestyle support, and strong social connections. Many people live stable and satisfying lives with long term treatment.
How does schizophrenia affect daily life
Schizophrenia can affect focus, communication, emotional responses, and social relationships. A person may struggle with work or school. Daily routines may feel overwhelming. With the right care and support, many people learn coping strategies that make daily life easier.
What types of hallucinations are common in schizophrenia
Auditory hallucinations are the most common. This means hearing voices that others cannot hear. Some people also experience visual hallucinations, such as seeing shapes or figures. Others may sense smells, tastes, or physical sensations without a physical source.
Why do people with schizophrenia develop delusions
Delusions are caused by changes in brain chemistry that affect how someone interprets information. A person may believe things that are not real because thoughts, perception, and logic become disrupted. These beliefs feel completely true to the person.
What support helps a person with schizophrenia the most
Support that helps includes therapy, medication management, family education, a structured routine, stress reduction, and regular mental health checkups. Kind communication and patience from loved ones also play a major role in recovery.
How can families help someone who lives with schizophrenia
Families can help by staying calm, learning about the condition, encouraging treatment, creating routines, reducing stress in the home, and offering emotional support. Listening with patience helps the person feel understood and supported.
Is schizophrenia the same as multiple personality disorder
No. Schizophrenia is not related to multiple identity disorder. Schizophrenia involves hallucinations, delusions, and changes in thinking, while dissociative identity disorder involves separate identity states. They are completely different conditions.
Does schizophrenia get worse without treatment
Yes. Without treatment, symptoms may become more intense and more frequent. Early treatment makes a major difference in long term outcomes and can prevent serious episodes.
Can someone live a normal life with schizophrenia
Yes. Many people build relationships, hold jobs, complete school, and live fulfilling lives. Treatment, education, and support make stability possible. Recovery is a long term process, and each person’s journey is unique.
How long does schizophrenia last
Schizophrenia is a lifelong condition. Symptoms may come and go. With proper treatment and support, many people experience long periods of stability and improvement.
What age does schizophrenia usually start
Most cases begin between the late teens and early thirties. Early symptoms often appear before the first full episode. Some people show signs slightly earlier or later depending on genetics and life factors.
Can stress make schizophrenia symptoms worse
Yes. Stress can trigger or intensify symptoms. A calm environment and stress reduction techniques help manage the condition more effectively.
Related Mental Health References and Trusted Resources
1. National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
Article: Schizophrenia: Overview and Key Facts
Link: https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/schizophrenia
NIMH is one of the most credible sources for mental health information. Their schizophrenia page includes symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatment research. Search engines trust NIMH, making it an excellent outbound link.
2. Mayo Clinic
Article: Schizophrenia: Symptoms and Causes
Link: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/schizophrenia/symptoms-causes/syc-20354443
The Mayo Clinic provides medically reviewed, easy to read information. Their schizophrenia page covers diagnosis, complications, and treatment options. This is a top tier external reference.
3. Cleveland Clinic
Article: Schizophrenia: Understanding the Condition
Link: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4568-schizophrenia
Cleveland Clinic is another high DA medical source with expert reviewed guidance. Their article includes in depth sections on symptoms, causes, and long term management.
More Articles From The Mental Health Blogger
- “What Are the 10 Most Common Types of Mental Illness? A Beginner’s Guide with Examples” — https://www.mentalhealthblogger.com/what-are-the-10-most-common-types-of-mental-illness-a-beginners-guide-with-examples/
- “5 Ways to Break the Stigma Around Mental Health” — https://www.mentalhealthblogger.com/break-the-stigma-around-mental-health/
